©Adobe Stock/481445980
Système de planification des ressources de l’entreprise (ERP)
One small step towards digitalization, one giant leap towards demand planning!
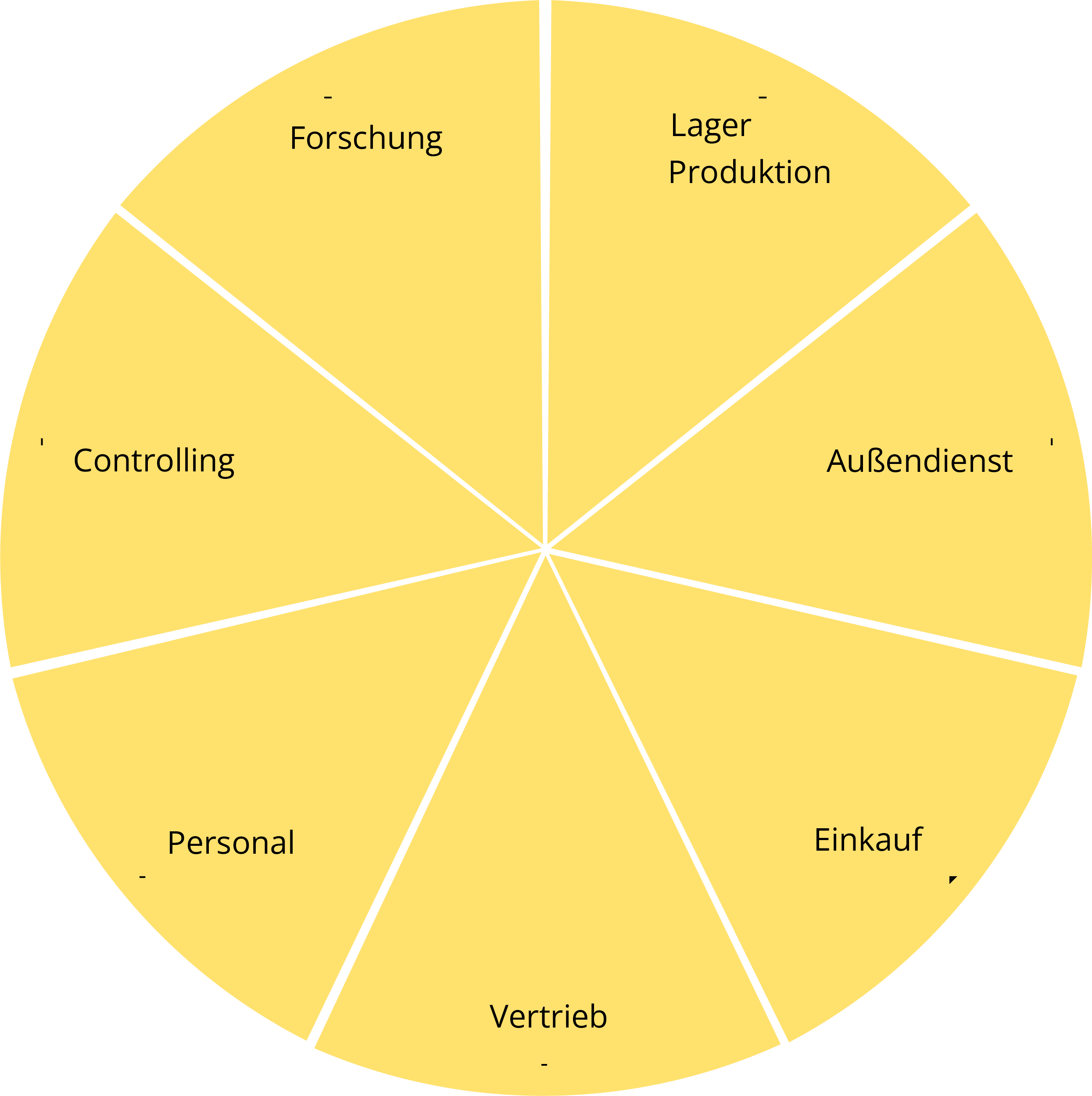
An enterprise resource planning system (ERP system) provides cross-functional support for all of a company’s business processes. IT consists of modules for the areas of procurement/Gestion des matières, production, sales, research and development, ressources humaines, finances et comptabilité, contrôle, etc. The modules are linked to each other via un common database and thus enable planning support across all company levels.
The current status
Questions about Enterprise Resource Planning
What do I need for ERP?
These are costs for materials and services.
plus
License fees for the software.
en ligne
solutions d’entreprise, a license starts at 15 EUR par user & month
Basically, the company needs an Connexion à l’internet.
OMS can do ERP?
There are two solutions from ERP.
Surpremise ERP:
Licenses are issued to specific persons and the software is permanently installed on a computer (Licenses are issued to specific persons and the software is permanently installed on a computer).
The computing power runs on the company’s own or rented servers.
OMS can
n, i
IS strongly dependent
on who
OMS owns a license and the software.
Nuage ERP:
Connexion internet stable avec un navigateur web (e.g. Firefox, Chrome, Microsoft Edge)
applications basées sur l’informatique en nuage can be accessed from anywhere.
Anyone who is granted access can use the system.
What can ERP do?
The possibilities can be expanded with modules. AS the name suggests, the basic functions relate to the resources of a company.
— Operating materials
— Capital
— Processus de travail
— Personnel
— Ressources
These elements are planned, controlled and monitored in the ERP system.
Application éventuelle scenarios
Introduction STEP-by-step
STEP 1: Sélecter le fournisseur
In which area should the ERP system be used?
Whould be recorded and monitored (paramètres should be recorded and monitored)?
Comment many people should have access?
STEP 2: Procédure d’examen
Create a small team of specialists from the various areas and positions.
They should include all processes that are to be adopted.
STEP 3: Environnement de test
TRY to apply the processes from step two.
Formulate good and bad aspects.
STEP 4: Customization
Make small software updates with the the
standardized
processes and collect master data that is required. Clean up the master data and enter it into the system.
Communicate the status of the project. Keep your colleagues up to date.
STEP 5: Documentation & training
Use tips to highlight the best aspects of the software (Use tips to highlight the best aspects of the software).
Train your employees and ensure that they work with it continuously.
STEP 6: Système réel
The specialists from the ERP project become the contact persons for application problems in the software.
STEP 7: Mises à jour
ADD further processes with software iterations.
The strengths of the software are only recognized with regular use
et asks for more.
Smaller updates can be introduced if employees make improvements.
Opportunités pour les PME
Contact us
Keep an eye on the most important SME-relevant technologies with our technology radar!
