©Adobe Stock/395167439
Cloud solution
Borderless opportunities!
The term cloud (German, cloud) or cloud computing describes an IT infrastructure consisting of multiple servers accessible via the internet or intranet and providing users with access to storage space, computing power or application software.
What is Cloud Computing?
Rapid scalability
Add or remove power in the shortest possible time.
Sharing of resources
Many users share a large pool of resources. This makes it possible to scale up in a flexible and cost-effective way.
Electorate
Data from the different users are separated from each other.
Metering
Regularisation and accurate billing.
Automation
Flexible scaling is only possible if the provider no longer needs to intervene and the processes are automated.
Bandwidth
Only useful with sufficient bandwidth (> 10 Mbps) or with mobile broadband (3G/4G).
State of play
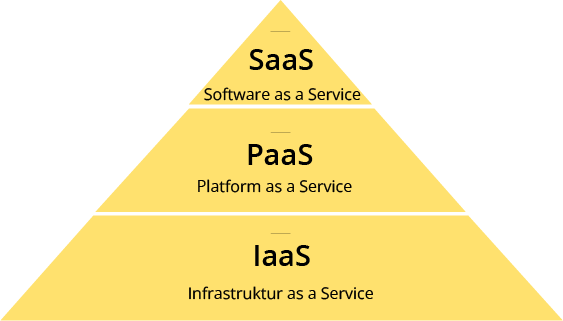
The term cloud, in daily use, has become a synonym for an unlimited online memory in which you can store his data and retrieve it from any device and location. However, the cloud can store much more than just data. For example, cloud computing in infrastructure can be distinguished as a service (IaaS), a platform as a service (PaaS) or software as a service (SaaS).
In terms of forms of access, we can distinguish between the two extreme private cloud and public cloud or the medium solution of the hybrid cloud.
Public Cloud
When a cloud is accessible to everyone by a public provider via the internet, it is referred to as a public cloud. Due to the large number of suppliers, there is a large portfolio of different offers in this model variant, which can be accessed without great effort. In this form of cloud, services are shared with other users and companies and have only a limited possibility to adapt to their own needs. This results in economies of scale through the use of many other users, which in turn lead to low prices in the applications. It is also possible that in this case the billing of the services can be accurate and that this does not entail any costs for businesses for unused services.
Private cloud
Unlike the public cloud, the private cloud can only be used for a specific group of people. For example, these cloud environments are often created by companies and used only by their own staff. The IT resources are located in the company’s own company and the cloud behind the company’s own firewall and can be used by staff via the intranet. For example, this execution has the typical advantages such as scalable IT structures or the possibility of installation and maintenance of the applications via the web browser. At the same time, however, the company must take over the IT structure and its maintenance itself.
Hybrid Cloud
The hybrid cloud is a mixed form of public and private cloud that combines benefits from both forms. In this model, the business processes can be divided into two categories. Data protection critical and non-critical processes. Depending on the division of the process, they can now be assigned to the public or private cloud variant. While this model variant includes all the benefits of public and private cloud, the complexity of the IT infrastructure and the management burden of managing this solution are increasing.
As an example of application of cloud computing, a company could outsource many parts of its IT structure to the cloud. For example, the cloud offers the possibility to access software that requires a powerful computer without the user having it at all. In particular, smaller companies can avoid expensive acquisition costs in the area of IT structure. There is no need for expensive and ever-growing server structures or IT staff to take care of their maintenance. Proper and accurate billing of the software used also ensures that the company only incurs costs if the services are actually used. To this end, accessibility via the internet makes it possible for staff to interact independently with cloud services independently.
Gradual introduction
Step 1: Identification of requirements
— Functional (e.g. what should the cloud solution be able to do?)
— Non-functional (e.g. technical and, above all, safety)
— Legal (e.g. data protection)
Requirements are clarified. It is also necessary to define all training requirements for staff in order to allow the switch to the new IT solution.
This profile will then enable suppliers to be compared with each other in the next step.
Step 2: Selection
Another important aspect is the analysis of cost-effectiveness and the associated assessment of whether the cloud solution can unlock potential and generate benefits.
Step 3: Introduction
Opportunities for SMEs
contact
Use our technology radar to keep a look at the main technologies relevant to SMEs!
