©Adobe Stock/571426637
Chatbots
Use of chatbots to automate customer communication
Chatbots are dialog systems with which you can communicate via text input or voice. They are often combined with Avatars and enable websites or instant messaging systems to automatically process inquiries from (potential) customers. In the long term, customer communication can be fully automated.
The current status
Until around 2016, Chatbots were mostly reserved for large companies, but they can now be found in small and medium-sized enterprises.
The challenge that Chatbots are currently facing is user acceptance. Many customers still prefer to be advised by a real person. But, this is changing as the technology becomes more widespread and reliable. According to to a survey conducted by Bitkom (German Association for Information Technology, Telecommunications and New Media) at the beginning of 2017, one in four Germans already could imagine using Chatbots.
Technology and use
Technology description
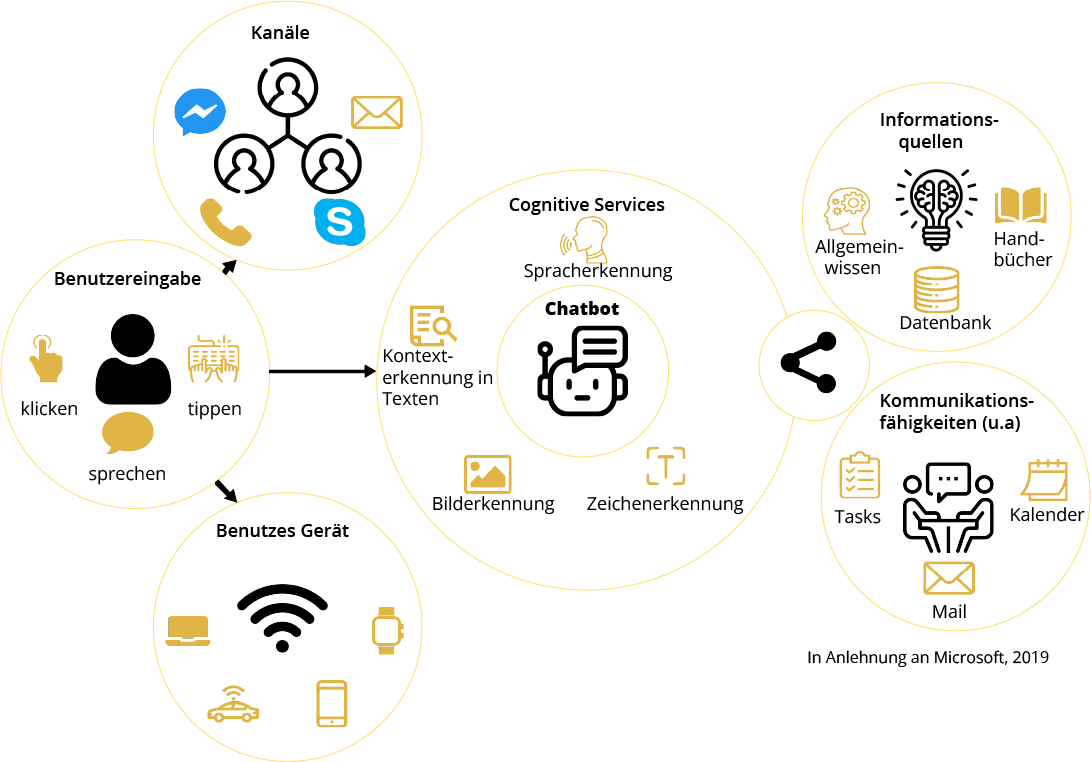
Possible application scenarios
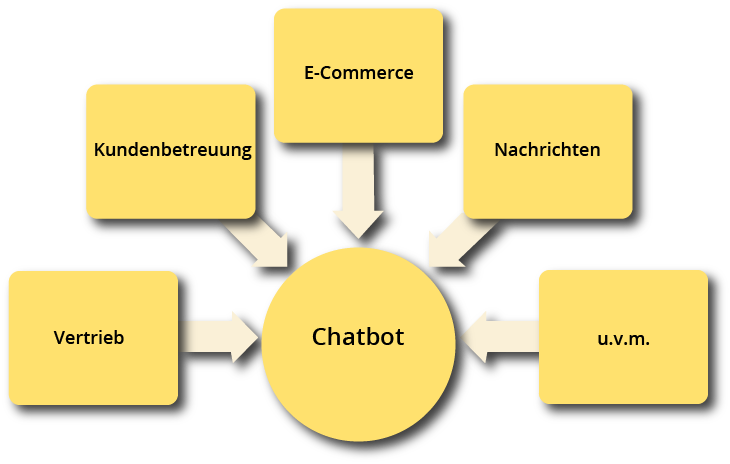
Chatbots provide services in various areas of the company. On the one hand, in direct contact with customers, i.e. in sales or e-commerce (smart & personal search function, assistance services such as sales promotion advice, instant service to answer questions, personalised customer care).
Another field of application is recruitment: chatbots facilitate communication with applicants and take the pressure off employees. In addition to communication tasks, the use of Chatbots is therefore common for organizational tasks such as scheduling or other routine tasks.
Step-by-step introduction
STEP1 Capture knowledge in a structured way
— Should it be possible for the Chatbot to answer questions about knowledge retrieval directly?
— Is it necessary to clarify by asking questions?
— is direct contact with a human consultant indispensable?
Step 2: Incorporated knowledge based on rules
Initial training of the chatbot
The knowledge database forms the basis for every information. This is where the actual information is stored in a structured manner. This is often done in the form of simple tables that contains question-answer pairs line by line.
Thanks to artificial intelligence, however, this does not necessarily have to be done manually, but can be automated on the basis of existing files or even existing structured websites.
Step 3: Mechanisms for refining detailed requests
Continuous training of the chatbot
Within the knowledge database, the artificial intelligence is inferred to recognise further formulation variants based on questions that have already been asked. The voice assistant always looks at how the questions are and calculates a degree of similarity for each user input. IF an automatic assignment is not possible because the match is too low, the Chatbot will ask for clarification.
Step 4: Self-learning improvement of answer options through AI
Opportunities for SMEs
Contact us
Keep an eye on the most important SME-relevant technologies with our technology radar!
