©Adobe Stock/571426637
Chatbots
Use of chatbots to automate customer communication
Chatbots are dialogue systems with which you can communicate through text or language. They are often combined with avatars and enable requests from (potential) customers to be processed automatically on websites or instant messaging systems. In the long term, customer communication can be fully automated.
State of play
Until around 2016, chatbots were mainly reserved for the big companies, but they are now also found in small and medium-sized enterprises.
The challenge that chatbots are facing at the moment is user acceptance. Many customers still prefer to be advised by a real person. However, as technology becomes more widespread and reliable, this is changing. At the beginning of 2017, according to a Bitkom survey (Bundesverband Informationswirtschaft, Telekommunikation und Neu Medien e.V.) already one out of four Germans to present chatbots.
Technology and deployment
Description of technology
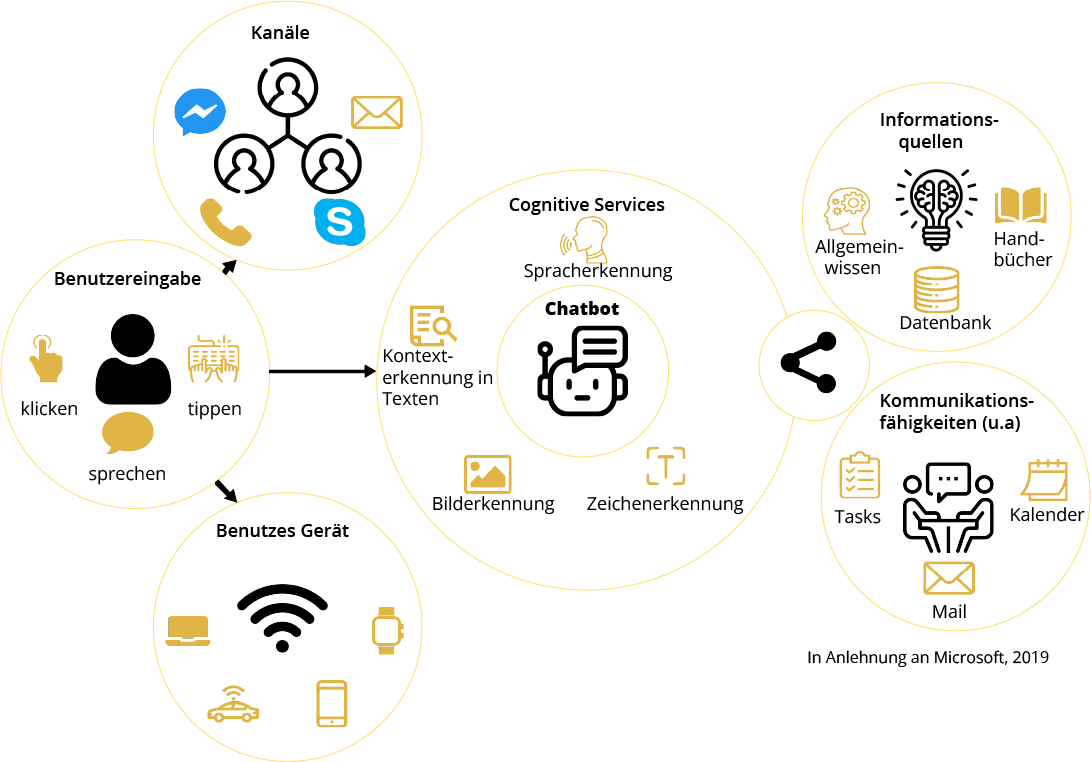
Possible use scenarios
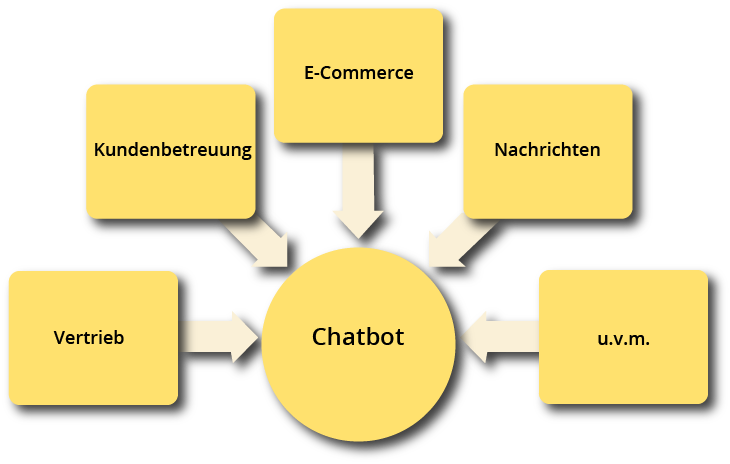
Chatbots take over services from various parts of the company. On the one hand, in direct contact with customers, i.e. in distribution or e-commerce (smart & personal search function, assistance services such as sales promotion advice, immediate answering services, personalised customer support).
Another field of application is recruitment: when contacting candidates, chatbots facilitate communication and relieve staff. In addition to communication tasks, the use of chatbots is also common for organisational tasks, such as scheduling or other routine tasks.
Gradual introduction
Step 1: Capturing knowledge structured
— should the possible questions on how to access the knowledge be answered directly by the chatbot?
— is there a need for clarification by means of enquiries?
— is it essential to have direct contact with a human advisor?
Step 2: Knowledge based on rules-based work
Initial training of the chatbot
The basis for each information offer is the knowledge base. It stores the actual information in a structured way. Often this is still done in the form of simple tables containing row-by-line Q & A pairs.
However, artificial intelligence does not necessarily have to do this manually, but can also be automated on the basis of existing files or even structured websites.
Step 3: Refinement mechanisms for detailed requests
Continuous training of the chatbot
Within the knowledge base, artificial intelligence is able to identify further formulation variants based on questions already asked. The Language Assistant always looks at how similar the questions are and calculates a match rate for each user input. If automatic assignment is not possible due to too low match, the chatbot will be clear with a query.
Step four: AI’s self-learning improvement of response options
Opportunities for SMEs
contact
Use our technology radar to keep a look at the main technologies relevant to SMEs!
